Charging 101
Don't give up on something just because you think you can't do it.
— Chanda Kochhar, CEO, ICICI
𐓏 Charging 101 𐓏
EV Charger types and specifications
The growth in demand for EVs in the world today has also led to the booming development of charging piles. However, just like the sockets in each country have different specifications, so when traveling abroad, you must purchase a travel adapter in advance.
Different countries and different car brands have slightly different specifications for charging connectors. Therefore, it is also very important to clarify the charging specifications of the car you had and the relevant local regulations.
𐓏 Charging 101 𐓏
EV Charger types and specifications
The growth in demand for EVs in the world today has also led to the booming development of charging piles. However, just like the sockets in each country have different specifications, so when traveling abroad, you must purchase a travel adapter in advance.
Different countries and different car brands have slightly different specifications for charging connectors. Therefore, it is also very important to clarify the charging specifications of the car you had and the relevant local regulations.
𐓏 Charging 101 𐓏
EV Charger types and specifications
The growth in demand for EVs in the world today has also led to the booming development of charging piles. However, just like the sockets in each country have different specifications, so when traveling abroad, you must purchase a travel adapter in advance.
Different countries and different car brands have slightly different specifications for charging connectors. Therefore, it is also very important to clarify the charging specifications of the car you had and the relevant local regulations.
1. Introduction to charging interface specifications in various countries

1. Introduction to charging interface specifications in various countries

1. Introduction to charging interface specifications in various countries

1.1 North American Charging Standard (NACS)
Designer
Tesla
Standard
SAE J3400
Charging Type
AC charging, DC charging
Area of use
All Countries except China and Europe
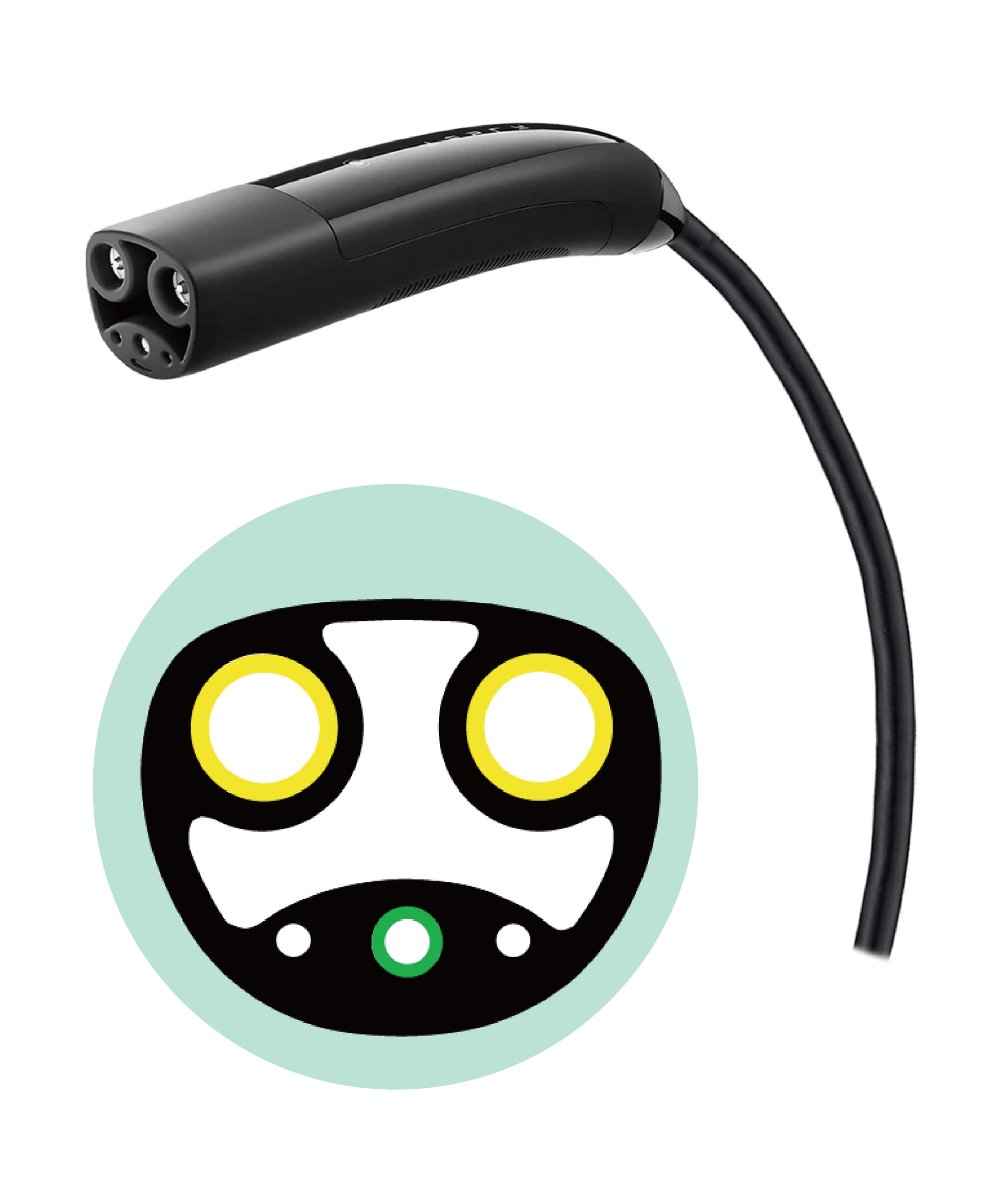

In 2012, Tesla developed a proprietary charging connector Tesla Proprietary Connector (TPC) for the Model S, which has also become a dedicated exclusive charging connector for Tesla models.
In 2022, the name has been changed to NACS and it is open to other manufacturers for free. In addition to welcoming more users to the original Tesla Supercharging Station, theyit also aspires to make NACS become a unified charging connector and technology in the North American market.
Source:Tesla NACS (visit the website)
1.1.1 Advantages
𖡡 Advanced design
Integrate AC and DC charging into the same charging interface for easy use.
𖡡 Huge charging network
Due to Tesla's high market share of EVs and relatively complete and extensive charging station settings, it was originally only available to Tesla owners. After it is opened in 2022, if other car manufacturers also use NACS connectors, they can directly provide the owners of their brands with a good and convenient charging experience.
𖡡 Improve overall costs
If NACS standards are unified, thanks to Tesla's existing huge charging network will be huge, which it will also significantly reduce the construction and operation costs of charging stations for other manufacturers.
𖡡 Popularization of EVs
As more car manufacturers adopt the NACS standard, the overall EV market expansion will accelerate, and it will promote the popularity of EVs.
1.1.2 Challenges
𖡡 Compatibility of Legacy device
Existing charging equipment and EVs may require conversion devices equipment to be compatible with the NACS standard.
𖡡 International standardization
NACS is primarily a charging standard for the North American market, so it may not be available in other regions.
1.1 North American Charging Standard (NACS)
Designer
Tesla
Standard
SAE J3400
Charging Type
AC charging, DC charging
Area of use
All Countries except China and Europe

In 2012, Tesla developed a proprietary charging connector Tesla Proprietary Connector (TPC) for the Model S, which has also become a dedicated exclusive charging connector for Tesla models.
In 2022, the name has been changed to NACS and it is open to other manufacturers for free. In addition to welcoming more users to the original Tesla Supercharging Station, theyit also aspires to make NACS become a unified charging connector and technology in the North American market.
Source:Tesla NACS (visit the website)
1.1.1 Advantages
𖡡 Advanced design
Integrate AC and DC charging into the same charging interface for easy use.
𖡡 Huge charging network
Due to Tesla's high market share of EVs and relatively complete and extensive charging station settings, it was originally only available to Tesla owners. After it is opened in 2022, if other car manufacturers also use NACS connectors, they can directly provide the owners of their brands with a good and convenient charging experience.
𖡡 Improve overall costs
If NACS standards are unified, thanks to Tesla's existing huge charging network will be huge, which it will also significantly reduce the construction and operation costs of charging stations for other manufacturers.
𖡡 Popularization of EVs
As more car manufacturers adopt the NACS standard, the overall EV market expansion will accelerate, and it will promote the popularity of EVs.
1.1.2 Challenges
𖡡 Compatibility of Legacy device
Existing charging equipment and EVs may require conversion devices equipment to be compatible with the NACS standard.
𖡡 International standardization
NACS is primarily a charging standard for the North American market, so it may not be available in other regions.
1.1 North American Charging Standard (NACS)
Designer
Tesla
Standard
SAE J3400
Charging Type
AC charging, DC charging
Area of use
All Countries except China and Europe

In 2012, Tesla developed a proprietary charging connector Tesla Proprietary Connector (TPC) for the Model S, which has also become a dedicated exclusive charging connector for Tesla models.
In 2022, the name has been changed to NACS and it is open to other manufacturers for free. In addition to welcoming more users to the original Tesla Supercharging Station, theyit also aspires to make NACS become a unified charging connector and technology in the North American market.
Source:Tesla NACS (visit the website)
1.1.1 Advantages
𖡡 Advanced design
Integrate AC and DC charging into the same charging interface for easy use.
𖡡 Huge charging network
Due to Tesla's high market share of EVs and relatively complete and extensive charging station settings, it was originally only available to Tesla owners. After it is opened in 2022, if other car manufacturers also use NACS connectors, they can directly provide the owners of their brands with a good and convenient charging experience.
𖡡 Improve overall costs
If NACS standards are unified, thanks to Tesla's existing huge charging network will be huge, which it will also significantly reduce the construction and operation costs of charging stations for other manufacturers.
𖡡 Popularization of EVs
As more car manufacturers adopt the NACS standard, the overall EV market expansion will accelerate, and it will promote the popularity of EVs.
1.1.2 Challenges
𖡡 Compatibility of Legacy device
Existing charging equipment and EVs may require conversion devices equipment to be compatible with the NACS standard.
𖡡 International standardization
NACS is primarily a charging standard for the North American market, so it may not be available in other regions.
1.2 Type 1 (SAE J1772)
Designer
Avcon
Yazaki Corporation
Standard
SAE J1772
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
North America, Japan, Taiwan
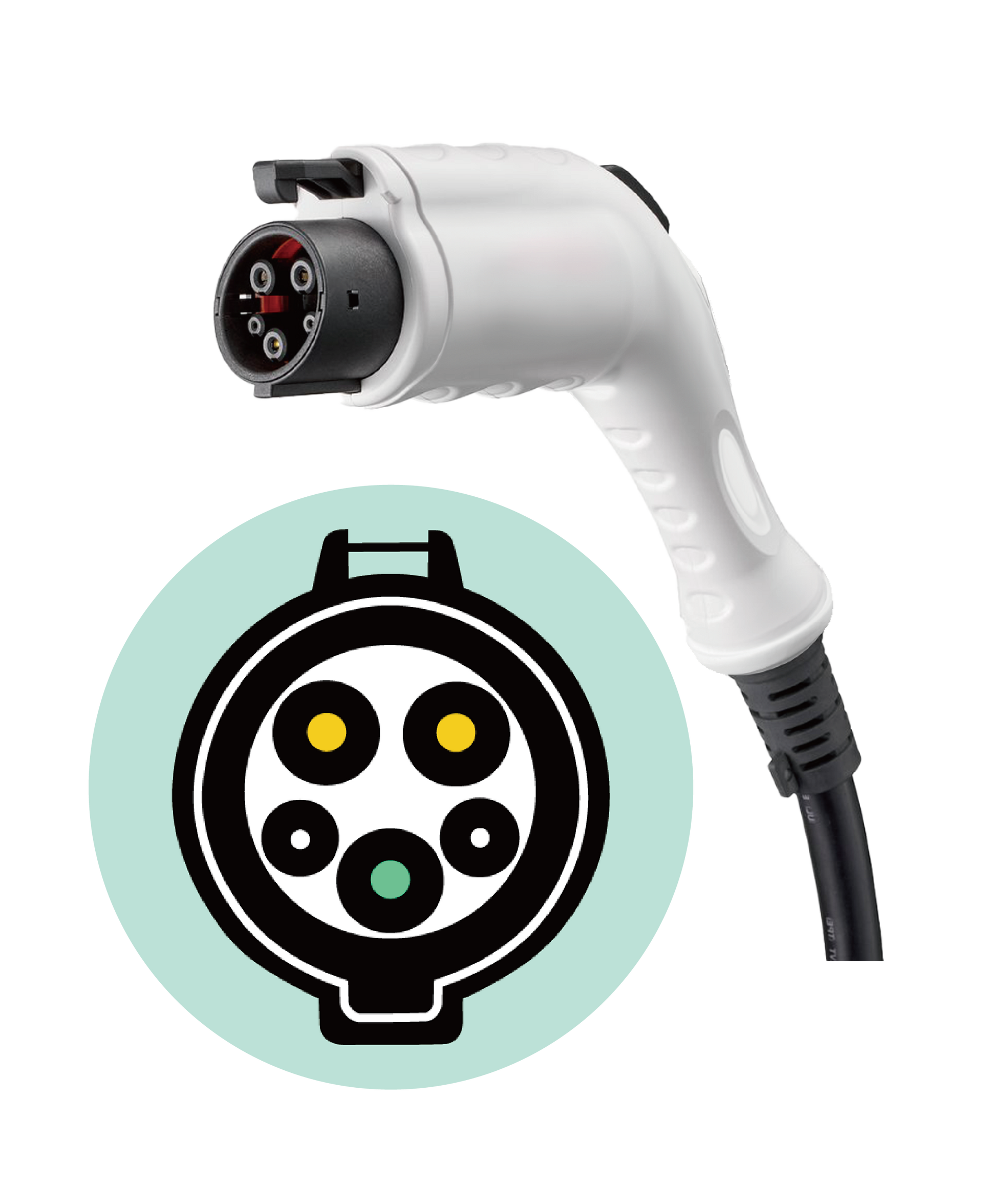

SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler.
Based on the SAE J1772 standard, the Japanese company Yazaki Corporation proposed a new design that improved the current limit of the early Avcon version. Therefore, the Type1 specification is sometimes called the "Type1 Yazaki plug"
Source:Yazaki (visit the website)
1.2.1 Advantages
𖡡 Widely applied
Type 1 is the charging standard in North America and is widely used in various EVs.
𖡡 High security
Multiple safety mechanisms are in place to ensure safe charging.
𖡡 Simple design
The plug design is simple, sturdy, and easy to operate.
1.2.2 Challenges
𖡡 Charging speed limit
Due to limited charging power and slow charging speed, it is only suitable for daily use and cannot meet fast charging needs.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The main regions of use are North America, Japan, and Taiwan. Other areas may require conversion devices.
1.2 Type 1 (SAE J1772)
Designer
Avcon
Yazaki Corporation
Standard
SAE J1772
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
North America, Japan, Taiwan

SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler.
Based on the SAE J1772 standard, the Japanese company Yazaki Corporation proposed a new design that improved the current limit of the early Avcon version. Therefore, the Type1 specification is sometimes called the "Type1 Yazaki plug".
Source:Yazaki (visit the website)
1.2.1 Advantages
𖡡 Widely applied
Type 1 is the charging standard in North America and is widely used in various EVs.
𖡡 High security
Multiple safety mechanisms are in place to ensure safe charging.
𖡡 Simple design
The plug design is simple, sturdy, and easy to operate.
1.2.2 Challenges
𖡡 Charging speed limit
Due to limited charging power and slow charging speed, it is only suitable for daily use and cannot meet fast charging needs.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The main regions of use are North America, Japan, and Taiwan. Other areas may require conversion devices.
1.2 Type 1 (SAE J1772)
Designer
Avcon
Yazaki Corporation
Standard
SAE J1772
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
North America, Japan, Taiwan

SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler.
Based on the SAE J1772 standard, the Japanese company Yazaki Corporation proposed a new design that improved the current limit of the early Avcon version. Therefore, the Type1 specification is sometimes called the "Type1 Yazaki plug".
Source:Yazaki (visit the website)
1.2.1 Advantages
𖡡 Widely applied
Type 1 is the charging standard in North America and is widely used in various EVs.
𖡡 High security
Multiple safety mechanisms are in place to ensure safe charging.
𖡡 Simple design
The plug design is simple, sturdy, and easy to operate.
1.2.2 Challenges
𖡡 Charging speed limit
Due to limited charging power and slow charging speed, it is only suitable for daily use and cannot meet fast charging needs.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The main regions of use are North America, Japan, and Taiwan. Other areas may require conversion devices.
1.3 Type 2 (Mennekes)
Designer
Mennekes Elektrotechnik GmbH & Co. KG
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, New Zealand, SEA Countries, Taiwan
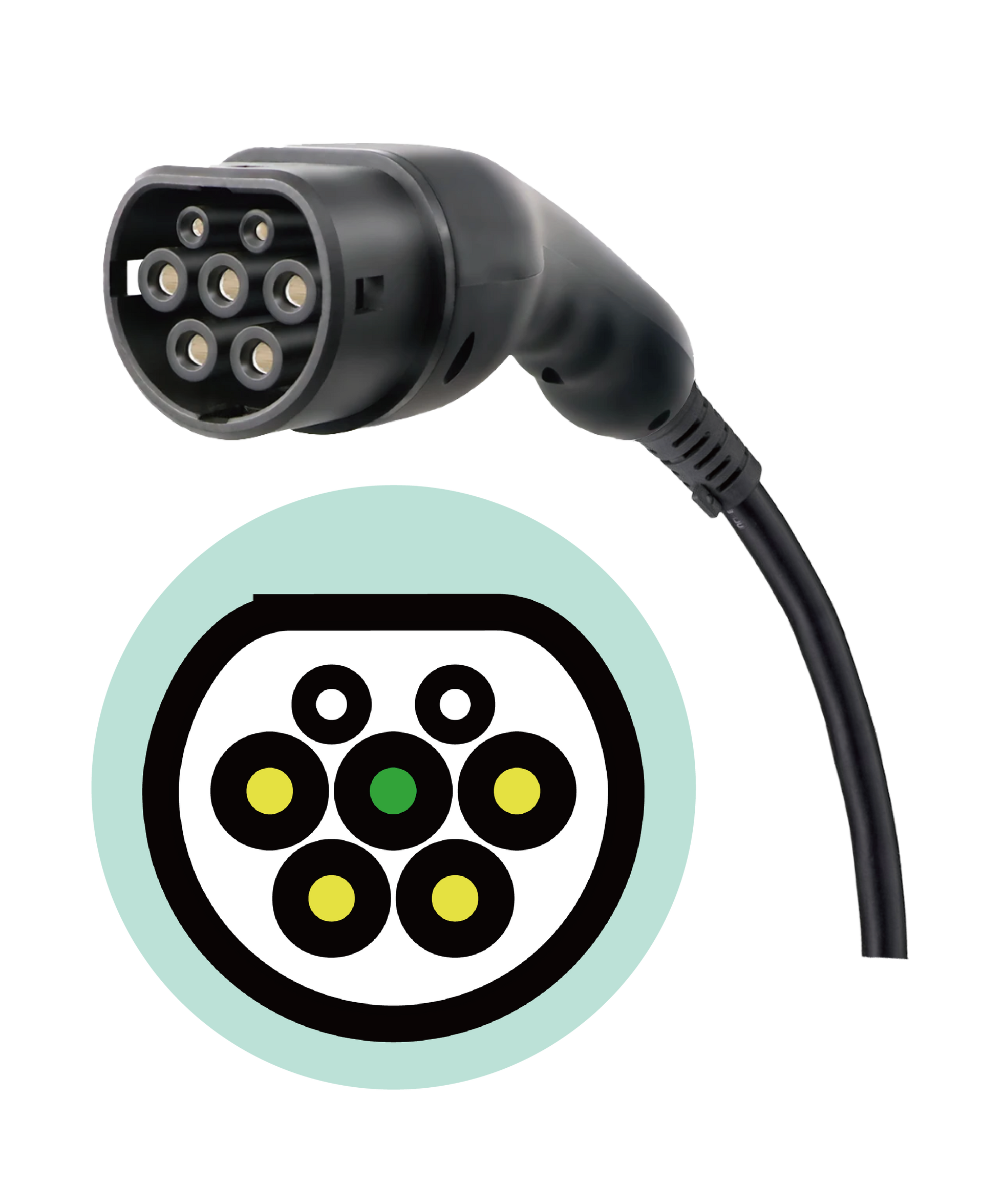

The Type 2 system was originally introducedproposed by the German company Mennekes in 2009. It features a side opening on the plug that enables the car and charger to automatically lock the plug to stay in place, preventing interruptions in charging and reducing the risk of cable theft.
In 2014, EU regulations mandated reqired that EVs must use the "Mennekes charging specification," which has hencesince become the standard across Europe. This regulation has beenis crucial for in the development of standardized EV infrastructure and charging systems throughout the region.
Source:Mennekes (visit the website)
1.3.1 Advantages
𖡡 Wide compatibility
Many EVs adopt Type2 interface, especially in the European market.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Type 2 design can provide V2G (vehicle to grid) technology, which can be used for energy regulation and storage applications.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
1.3.2 Challenges
𖡡 Standardization issues
Although Type 2 also has a high market share, since Type 1 is mainly used in North America, it still requires the assistance of a conversion device for charging.
𖡡 Higher installation costs
Because it provides a higher- power three-phase charging method, the relatinged installation costs are higher.
1.3 Type 2 (Mennekes)
Designer
Mennekes Elektrotechnik GmbH & Co. KG
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, New Zealand, SEA Countries, Taiwan

The Type 2 system was originally introducedproposed by the German company Mennekes in 2009. It features a side opening on the plug that enables the car and charger to automatically lock the plug to stay in place, preventing interruptions in charging and reducing the risk of cable theft.
In 2014, EU regulations mandated reqired that EVs must use the "Mennekes charging specification," which has hencesince become the standard across Europe. This regulation has beenis crucial for in the development of standardized EV infrastructure and charging systems throughout the region.
Source:Mennekes (visit the website)
1.3.1 Advantages
𖡡 Wide compatibility
Many EVs adopt Type2 interface, especially in the European market.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Type 2 design can provide V2G (vehicle to grid) technology, which can be used for energy regulation and storage applications.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
1.3.2 Challenges
𖡡 Standardization issues
Although Type 2 also has a high market share, since Type 1 is mainly used in North America, it still requires the assistance of a conversion device for charging.
𖡡 Higher installation costs
Because it provides a higher- power three-phase charging method, the relatinged installation costs are higher.
1.3 Type 2 (Mennekes)
Designer
Mennekes Elektrotechnik GmbH & Co. KG
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, New Zealand, SEA Countries, Taiwan

The Type 2 system was originally introducedproposed by the German company Mennekes in 2009. It features a side opening on the plug that enables the car and charger to automatically lock the plug to stay in place, preventing interruptions in charging and reducing the risk of cable theft.
In 2014, EU regulations mandated reqired that EVs must use the "Mennekes charging specification," which has hencesince become the standard across Europe. This regulation has beenis crucial for in the development of standardized EV infrastructure and charging systems throughout the region.
Source:Mennekes (visit the website)
1.3.1 Advantages
𖡡 Wide compatibility
Many EVs adopt Type2 interface, especially in the European market.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Type 2 design can provide V2G (vehicle to grid) technology, which can be used for energy regulation and storage applications.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
1.3.2 Challenges
𖡡 Standardization issues
Although Type 2 also has a high market share, since Type 1 is mainly used in North America, it still requires the assistance of a conversion device for charging.
𖡡 Higher installation costs
Because it provides a higher- power three-phase charging method, the relatinged installation costs are higher.
1.4 CCS1 (Combined Charging System 1)
Designer
CharIN Association
Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE International)
Standard
SAE J1772
IEC 62196-3 EE
Charging Type
DC charging
Support Type1 AC charging
Area of use
North America, Central America, South Korea, Taiwan
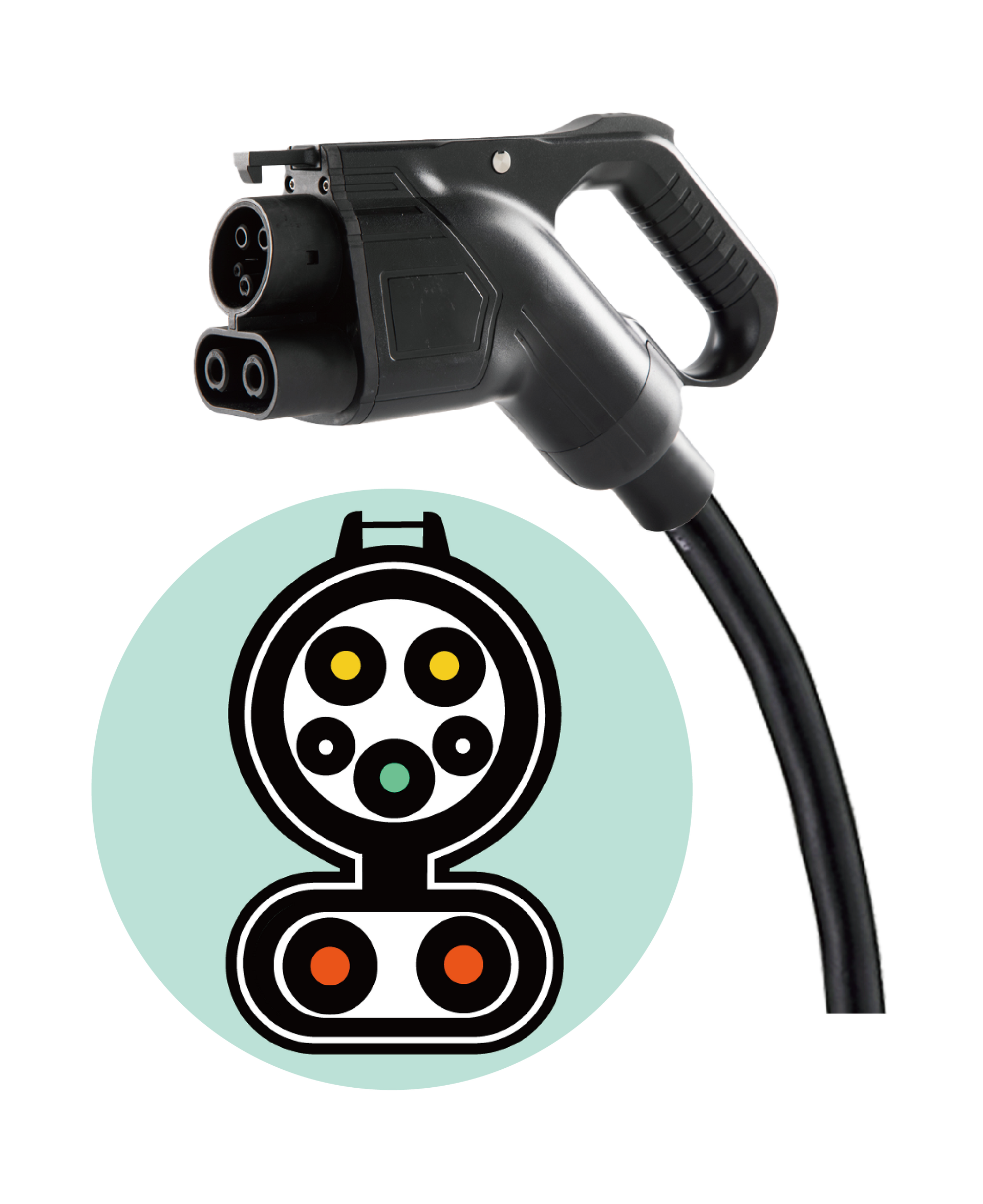

The CCS (Combined Charging System) charging standard was jointly developed by members of the CharIN Association (Charging Interface Initiative), which includes many major automobile manufacturers and technology companies, such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Ford, and Volkswagen AG (Including Audi, Porsche), GM, Tesla, EVgo, Delta, Infineon, etc. The purpose of the development is to provide a comprehensive solution that can perform both AC and DC charging.
CCS1 combines Type 1, shares the SAE J1772 standard, and adds two DC pins below to provide DC charging function. CCS1 is one of the most common charging specifications in the United States.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.4.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
Supports DC charging and Type1 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Designed for high-power charging, it significantly reduces the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in North America and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.4.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions and compatibility
It is mainly used in North America. In areas like Europe using CCS2 specificationsIf other charging specifications such as CCS2 are used, a conversion device is required.
𖡡 High construction cost
The purchase and maintenance costs of high-power DC charging equipment are relatively high, soand the home users need tomay consider the necessity of setting them up such DC Chargers.
1.4 CCS1 (Combined Charging System 1)
Designer
CharIN Association
Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE International)
Standard
SAE J1772
IEC 62196-3 EE
Charging Type
DC charging
Support Type1 AC charging
Area of use
North America, Central America, South Korea, Taiwan

The CCS (Combined Charging System) charging standard was jointly developed by members of the CharIN Association (Charging Interface Initiative), which includes many major automobile manufacturers and technology companies, such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Ford, and Volkswagen AG (Including Audi, Porsche), GM, Tesla, EVgo, Delta, Infineon, etc. The purpose of the development is to provide a comprehensive solution that can perform both AC and DC charging.
CCS1 combines Type 1, shares the SAE J1772 standard, and adds two DC pins below to provide DC charging function. CCS1 is one of the most common charging specifications in the United States.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.4.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
Supports DC charging and Type1 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Designed for high-power charging, it significantly reduces the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in North America and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.4.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions and compatibility
It is mainly used in North America. In areas like Europe using CCS2 specificationsIf other charging specifications such as CCS2 are used, a conversion device is required.
𖡡 High construction cost
The purchase and maintenance costs of high-power DC charging equipment are relatively high, soand the home users need tomay consider the necessity of setting them up such DC Chargers.
1.4 CCS1 (Combined Charging System 1)
Designer
CharIN Association
Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE International)
Standard
SAE J1772
IEC 62196-3 EE
Charging Type
DC charging
Support Type1 AC charging
Area of use
North America, Central America, South Korea, Taiwan

The CCS (Combined Charging System) charging standard was jointly developed by members of the CharIN Association (Charging Interface Initiative), which includes many major automobile manufacturers and technology companies, such as BMW, Mercedes-Benz, Ford, and Volkswagen AG (Including Audi, Porsche), GM, Tesla, EVgo, Delta, Infineon, etc. The purpose of the development is to provide a comprehensive solution that can perform both AC and DC charging.
CCS1 combines Type 1, shares the SAE J1772 standard, and adds two DC pins below to provide DC charging function. CCS1 is one of the most common charging specifications in the United States.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.4.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
Supports DC charging and Type1 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Designed for high-power charging, it significantly reduces the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in North America and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.4.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions and compatibility
It is mainly used in North America. In areas like Europe using CCS2 specificationsIf other charging specifications such as CCS2 are used, a conversion device is required.
𖡡 High construction cost
The purchase and maintenance costs of high-power DC charging equipment are relatively high, soand the home users need tomay consider the necessity of setting them up such DC Chargers.
1.5 CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2)
Designer
CharIN Association
The European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA)
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
IEC 62196-3 FF
Charging Type
DC Charging
Support Type2 AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, South America, South Africa, the Middle East, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, etc.
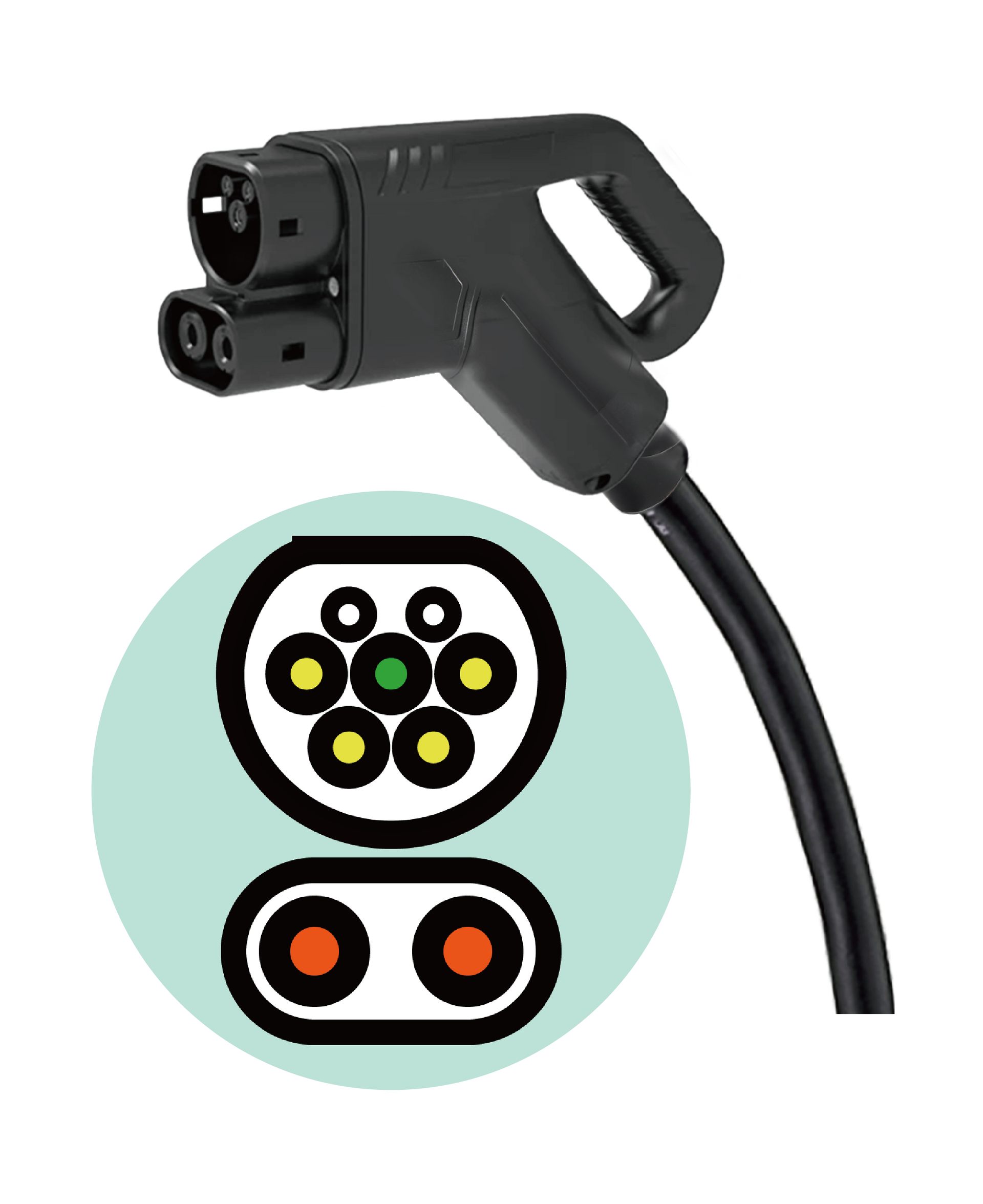
CCS2 is a DC charging standard widely used in Europe and other regions. It combines Type 2 and shares the IEC 62196-2 Type 2 standard and adds two DC pins below to provide a DC charging function.
In May 2012, ACEA approved the standardization of CCS2 charging specifications across the European Union.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.5.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
In addition to DC charging, it also supports Type2 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Because it is designed for high-power charging, the charging time can be greatly shortened.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in Europe and many regions, and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.5.2 Challenges
𖡡 High construction cost
High-power DC charging equipment comes with significanthigh purchase and maintenance costs, so owners should evaluate whether the installation is necessary.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The Type 2 standard is primarily used in Europe and other regions that adopt it. Consequently, aAreas like North America that use CCS1 require conversion devices for compatibility.
1.5 CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2)
Designer
CharIN Association
The European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA)
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
IEC 62196-3 FF
Charging Type
DC Charging
Support Type2 AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, South America, South Africa, the Middle East, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, etc.

CCS2 is a DC charging standard widely used in Europe and other regions. It combines Type 2 and shares the IEC 62196-2 Type 2 standard and adds two DC pins below to provide a DC charging function.
In May 2012, ACEA approved the standardization of CCS2 charging specifications across the European Union.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.5.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
In addition to DC charging, it also supports Type2 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Because it is designed for high-power charging, the charging time can be greatly shortened.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in Europe and many regions, and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.5.2 Challenges
𖡡 High construction cost
High-power DC charging equipment comes with significanthigh purchase and maintenance costs, so owners should evaluate whether the installation is necessary.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The Type 2 standard is primarily used in Europe and other regions that adopt it. Consequently, aAreas like North America that use CCS1 require conversion devices for compatibility.
1.5 CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2)
Designer
CharIN Association
The European Automobile Manufacturers' Association (ACEA)
Standard
IEC 62196-2 Type 2
IEC 62196-3 FF
Charging Type
DC Charging
Support Type2 AC charging
Area of use
Europe, Australia, South America, South Africa, the Middle East, India, Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, etc.

CCS2 is a DC charging standard widely used in Europe and other regions. It combines Type 2 and shares the IEC 62196-2 Type 2 standard and adds two DC pins below to provide a DC charging function.
In May 2012, ACEA approved the standardization of CCS2 charging specifications across the European Union.
Source:CharIN (visit the website)
1.5.1 Advantages
𖡡 Versatility
In addition to DC charging, it also supports Type2 AC charging.
𖡡 Fast charging time
Because it is designed for high-power charging, the charging time can be greatly shortened.
𖡡 Widely applied
It is the main standard for fast charging in Europe and many regions, and is widely adopted by car manufacturers.
1.5.2 Challenges
𖡡 High construction cost
High-power DC charging equipment comes with significanthigh purchase and maintenance costs, so owners should evaluate whether the installation is necessary.
𖡡 Regional restrictions
The Type 2 standard is primarily used in Europe and other regions that adopt it. Consequently, aAreas like North America that use CCS1 require conversion devices for compatibility.
1.6 CHAdeMO
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
Standard
CHAdeMO 0.9 ~ CHAdeMO 2.0
IEC 62196-3 AA
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
Japan, Taiwan, the United States, Canada, and some European countries
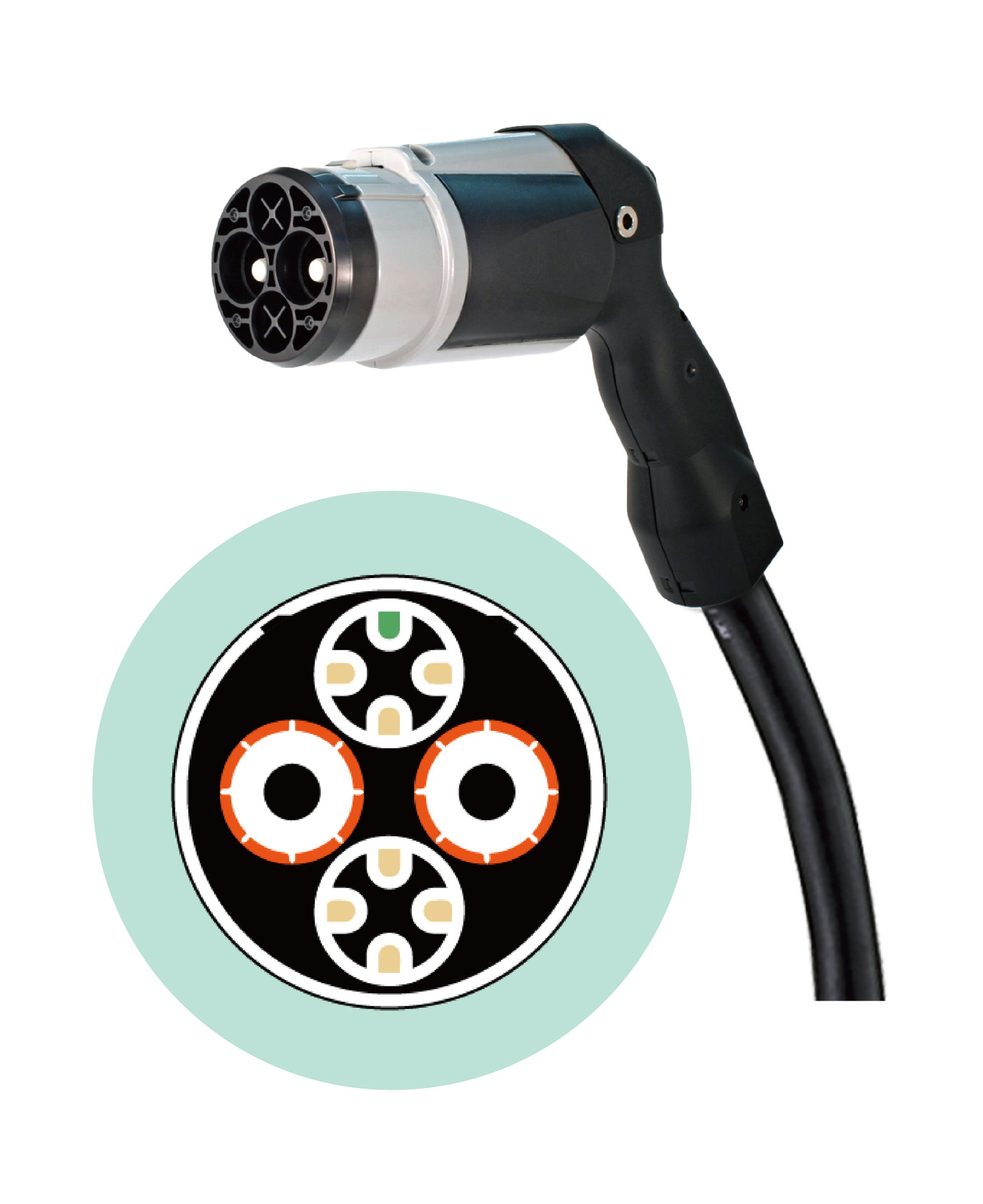

CHAdeMO is a charging technology standard proposed by the Japanese Association-CHAdeMO in 2010. Based on the expansion of this technology, many versions of protocols have been developed and applied to different levels and categories of EVs.
According to the CHAdeMO official website, most global chargers deployed globally currently use the CHAdeMO 0.9 protocol standard. CHAdeMO 1.2 supports charging up to 200 kW, while CHAdeMO 2.0 offers high-power charging of up to 400 kW, suitable for large commercial vehicles.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.6.1 Advantages
𖡡 Fast charging
Supports high-power DC charging, significantly reducing charging time.
𖡡 High reliability
Since 2006, there have been many test plans for related technologies, and after years of application and improvement, it has a high degree of reliability and stability.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Provides V2G (vehicle-to-grid) technology and V2H (vehicle-to-home) technology; it is significant of great significance for energy regulation and energy storage applications.
1.6.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions
It is mainly used in Japan and some European countries, and its popularity in other regions is low.
𖡡 Market competition
With the rapid adoption of other charging standards worldwide, CHAdeMO is experiencing increasing competitive pressure.
𖡡 Construction costs are higher
The construction and maintenance costs of high-power DC fast charging stations are relatively high.
1.6 CHAdeMO
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
Standard
CHAdeMO 0.9 ~ CHAdeMO 2.0
IEC 62196-3 AA
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
Japan, Taiwan, the United States, Canada, and some European countries

CHAdeMO is a charging technology standard proposed by the Japanese Association-CHAdeMO in 2010. Based on the expansion of this technology, many versions of protocols have been developed and applied to different levels and categories of EVs.
According to the CHAdeMO official website, most global chargers deployed globally currently use the
CHAdeMO 0.9 protocol standard. CHAdeMO 1.2 supports charging up to 200 kW, while CHAdeMO 2.0 offers high-power charging of up to 400 kW, suitable for large commercial vehicles.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.6.1 Advantages
𖡡 Fast charging
Supports high-power DC charging, significantly reducing charging time.
𖡡 High reliability
Since 2006, there have been many test plans for related technologies, and after years of application and improvement, it has a high degree of reliability and stability.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Provides V2G (vehicle-to-grid) technology and V2H (vehicle-to-home) technology; it is significant of great significance for energy regulation and energy storage applications.
1.6.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions
It is mainly used in Japan and some European countries, and its popularity in other regions is low.
𖡡 Market competition
With the rapid adoption of other charging standards worldwide, CHAdeMO is experiencing increasing competitive pressure.
𖡡 Construction costs are higher
The construction and maintenance costs of high-power DC fast charging stations are relatively high.
1.6 CHAdeMO
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
Standard
CHAdeMO 0.9 ~ CHAdeMO 2.0
IEC 62196-3 AA
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
Japan, Taiwan, the United States, Canada, and some European countries

CHAdeMO is a charging technology standard proposed by the Japanese Association-CHAdeMO in 2010. Based on the expansion of this technology, many versions of protocols have been developed and applied to different levels and categories of EVs.
According to the CHAdeMO official website, most global chargers deployed globally currently use the
CHAdeMO 0.9 protocol standard. CHAdeMO 1.2 supports charging up to 200 kW, while CHAdeMO 2.0 offers high-power charging of up to 400 kW, suitable for large commercial vehicles.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.6.1 Advantages
𖡡 Fast charging
Supports high-power DC charging, significantly reducing charging time.
𖡡 High reliability
Since 2006, there have been many test plans for related technologies, and after years of application and improvement, it has a high degree of reliability and stability.
𖡡 Bidirectional charging
Provides V2G (vehicle-to-grid) technology and V2H (vehicle-to-home) technology; it is significant of great significance for energy regulation and energy storage applications.
1.6.2 Challenges
𖡡 Regional restrictions
It is mainly used in Japan and some European countries, and its popularity in other regions is low.
𖡡 Market competition
With the rapid adoption of other charging standards worldwide, CHAdeMO is experiencing increasing competitive pressure.
𖡡 Construction costs are higher
The construction and maintenance costs of high-power DC fast charging stations are relatively high.
1.7 GB/T AC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
China
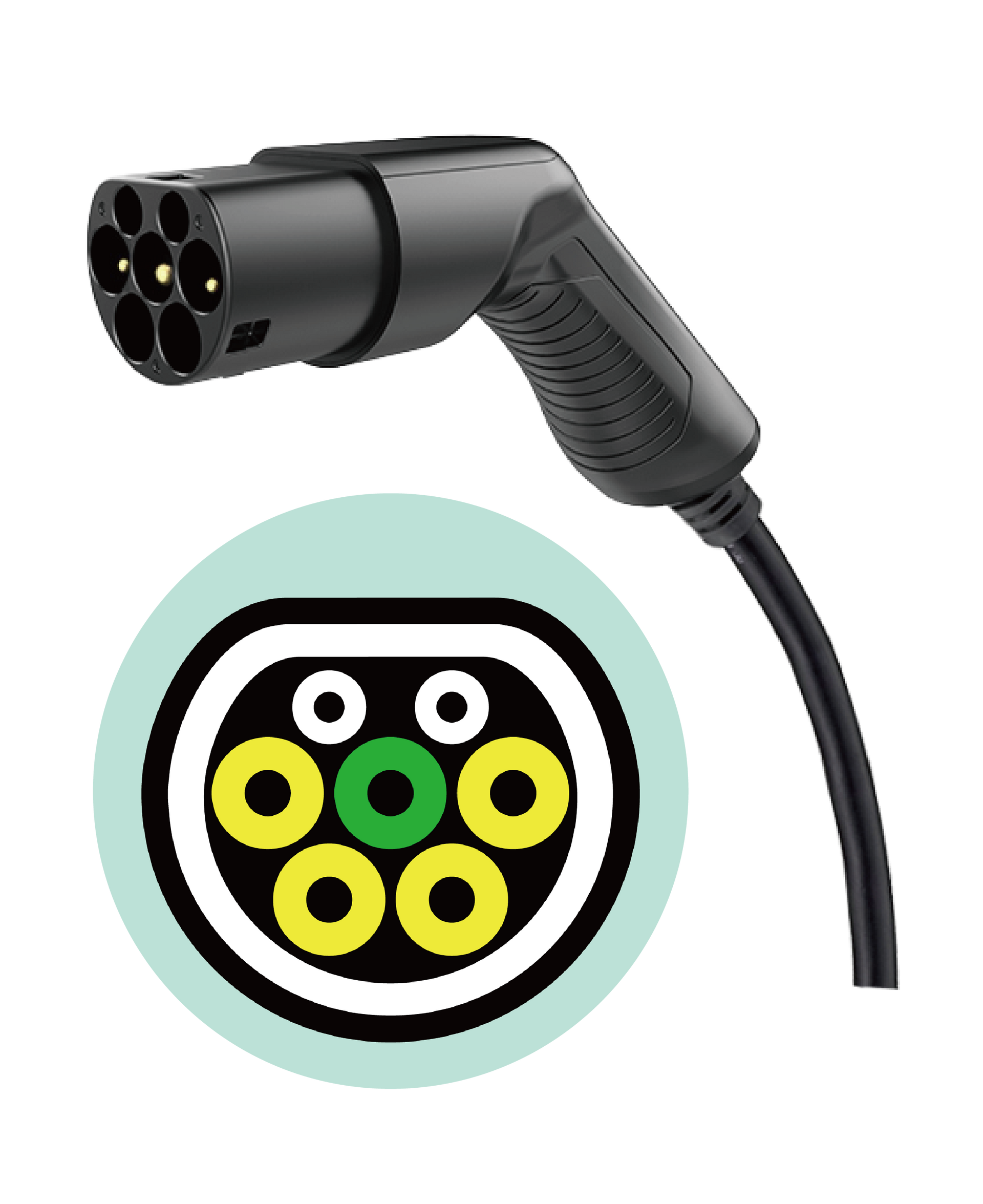

AC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
GB/T is a "recommended national standard" for charging piles, independently developed and promoted by China. Approved by the Standardization Administration Committee (SAC) and formulated by the administrative departments for standardization of the State Council of China, it meets basic requirements and aligns with mandatory national standards. It also incorporates the technical specifications necessary to lead various related industries.
AC charging uses the GB/T 20234.2 standard, which is similar to Type 2, but has some differences in signal and configuration.
1.7.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.7.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Since there is a certain cost in the construction and maintenance of charging stations, this may affect the speed of promotion in some areas.
1.7 GB/T AC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
China

AC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
GB/T is a "recommended national standard" for charging piles, independently developed and promoted by China. Approved by the Standardization Administration Committee (SAC) and formulated by the administrative departments for standardization of the State Council of China, it meets basic requirements and aligns with mandatory national standards. It also incorporates the technical specifications necessary to lead various related industries.
AC charging uses the GB/T 20234.2 standard, which is similar to Type 2, but has some differences in signal and configuration.
1.7.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.7.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Since there is a certain cost in the construction and maintenance of charging stations, this may affect the speed of promotion in some areas.
1.7 GB/T AC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.2
Charging Type
AC charging
Area of use
China

AC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
GB/T is a "recommended national standard" for charging piles, independently developed and promoted by China. Approved by the Standardization Administration Committee (SAC) and formulated by the administrative departments for standardization of the State Council of China, it meets basic requirements and aligns with mandatory national standards. It also incorporates the technical specifications necessary to lead various related industries.
AC charging uses the GB/T 20234.2 standard, which is similar to Type 2, but has some differences in signal and configuration.
1.7.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Supports higher power AC charging
In three-phase charging, the charging speed is significantly improved.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.7.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Since there is a certain cost in the construction and maintenance of charging stations, this may affect the speed of promotion in some areas.
1.8 GB/T DC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China
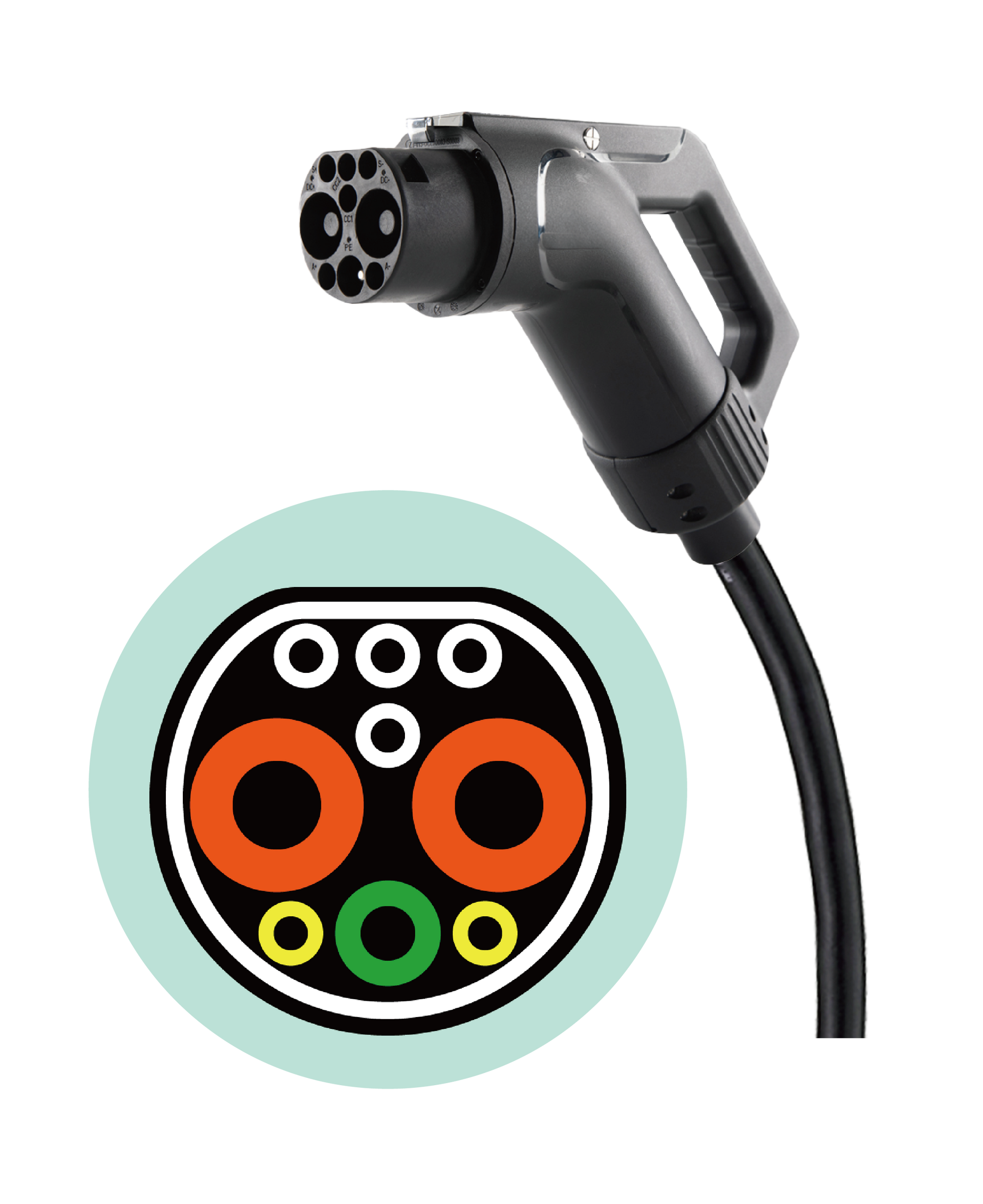
DC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
According to the GB/T standard, DC charging is larger than AC charging and adopts the GB/T 20234.3 standard, which is efficient, safe, and reliable.
Chinese EVs manufacturers including BYD, NIO, and XPeng Motors, as well as EV brands sold in China, all support the GB/T DC charging standard.
1.8.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Fast charging
The design supports high-power DC charging, which can greatly shorten the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.8.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Due to the construction and maintenance costs of charging stations, the speed of their promotion may be affected in some areas.
1.8 GB/T DC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China

DC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
According to the GB/T standard, DC charging is larger than AC charging and adopts the GB/T 20234.3 standard, which is efficient, safe, and reliable.
Chinese EVs manufacturers including BYD, NIO, and XPeng Motors, as well as EV brands sold in China, all support the GB/T DC charging standard.
1.8.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Fast charging
The design supports high-power DC charging, which can greatly shorten the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.8.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Due to the construction and maintenance costs of charging stations, the speed of their promotion may be affected in some areas.
1.8 GB/T DC
Designer
Standardization Administration of China (SAC)
Standard
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China

DC charging pile standards formulated by the National Standards of the People's Republic of China (Chinese spelling: Guó Biāo , GB)
According to the GB/T standard, DC charging is larger than AC charging and adopts the GB/T 20234.3 standard, which is efficient, safe, and reliable.
Chinese EVs manufacturers including BYD, NIO, and XPeng Motors, as well as EV brands sold in China, all support the GB/T DC charging standard.
1.8.1 Advantages
𖡡 National standards
Developed by the China National Standardization Administration Committee, it unifies the regulations within China and contributes to the popularization of EVs.
𖡡 Fast charging
The design supports high-power DC charging, which can greatly shorten the charging time.
𖡡 Widely applied
As a national standard, it has been widely promoted and applied among EVs in China.
1.8.2 Challenges
𖡡 International compatibility
Mainly used in the Chinese market, it is not fully compatible with other international charging standards and needs to be charged through an adapter, which may limit the convenience penetration of charging in the Chinese charging insdustires charging car market into the international market.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
Due to the construction and maintenance costs of charging stations, the speed of their promotion may be affected in some areas.
1.9 ChaoJi
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
China Electricity Council (CEC)
Standard
CHAdeMO 3.0
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China, Japan and other regions.
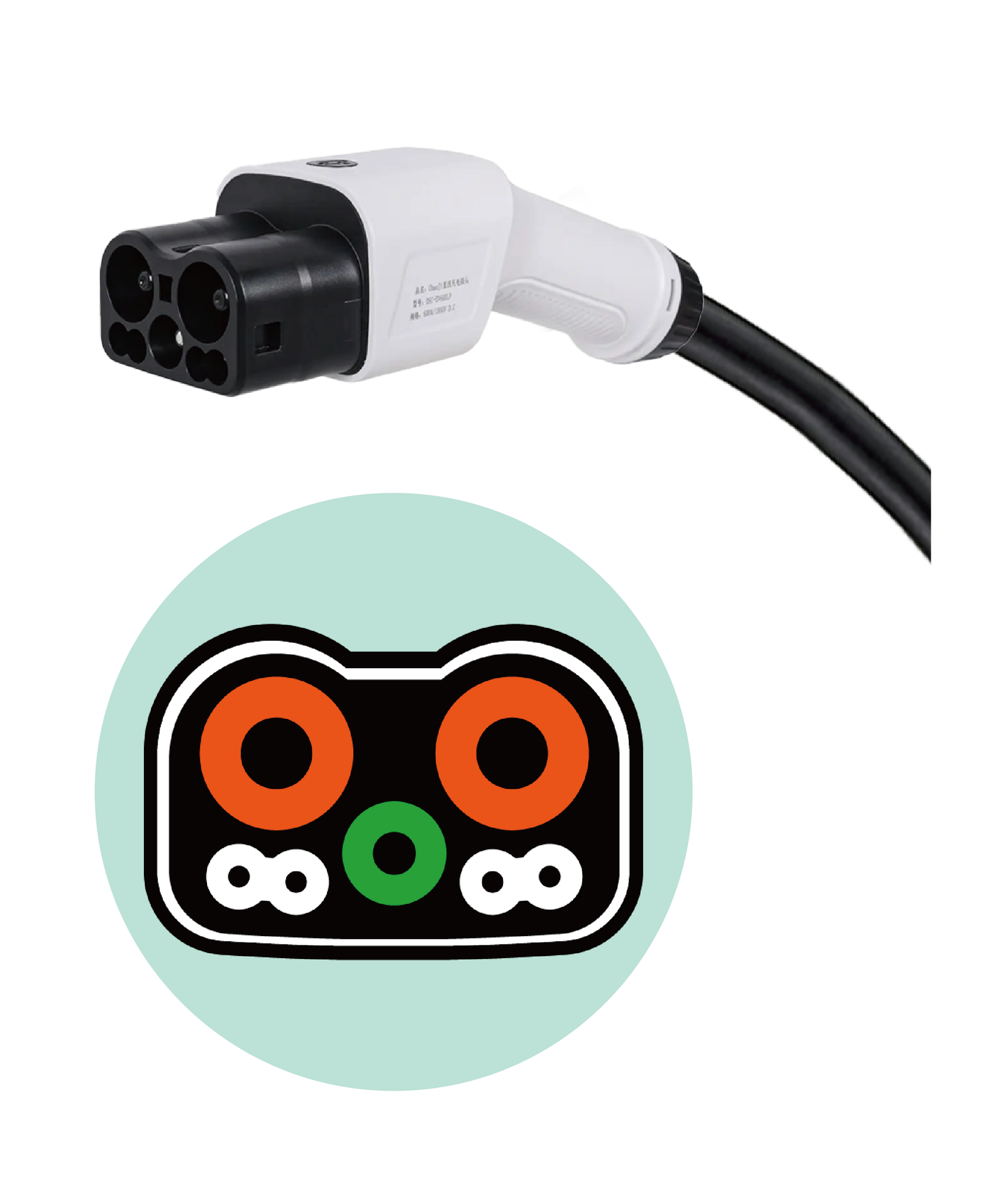

In 2020, the China Electricity Council (CEC) collaborated with the CHAdeMO Association to launch a high-power fast charging system interface called ChaoJi, also known as CHAdeMO 3.0. The first charging test and demonstration were completed, and the full specifications were officially released in April 2021.
ChaoJi can achieve 500kW high-power charging. The latest version in 2023 is ChaoJi-2/CHAdeMO 3.1, and Ultra-ChaoJi/CHAdeMO 4.0 is also under intensive rapid development.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.9.1 Advantages
𖡡 Support ultra-high power charging
The current maximum power can reach 900 kW, which can greatly shorten the charging time and adapt to the charging needs of large-capacity batteries in the future.
𖡡 Unified specifications
Jointly developed by China and Japan, the design is not only compatible with CHAdeMO and GB/T DC but also has a circuit interface design that is compatible with CCS. Therefore, it is regarded as laying the foundation for future global DC charging technology standardization.
𖡡 Compatibility
The design considers the existing charging standards and has high compatibility to facilitate transition and promotion.
1.9.2 Challenges
𖡡 Market promotion
As a new charging standard, it still needs to overcome the challenges of market acceptance and promotion speed.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
It is high-power charging, and the construction cost of charging stations is high, which may affect the speed of initial promotion.
1.9 ChaoJi
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
China Electricity Council (CEC)
Standard
CHAdeMO 3.0
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China, Japan and other regions.

In 2020, the China Electricity Council (CEC) collaborated with the CHAdeMO Association to launch a high-power fast charging system interface called ChaoJi, also known as CHAdeMO 3.0. The first charging test and demonstration were completed, and the full specifications were officially released in April 2021.
ChaoJi can achieve 500kW high-power charging. The latest version in 2023 is ChaoJi-2/CHAdeMO 3.1, and Ultra-ChaoJi/CHAdeMO 4.0 is also under intensive rapid development.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.9.1 Advantages
𖡡 Support ultra-high power charging
The current maximum power can reach 900 kW, which can greatly shorten the charging time and adapt to the charging needs of large-capacity batteries in the future.
𖡡 Unified specifications
Jointly developed by China and Japan, the design is not only compatible with CHAdeMO and GB/T DC but also has a circuit interface design that is compatible with CCS. Therefore, it is regarded as laying the foundation for future global DC charging technology standardization.
𖡡 Compatibility
The design considers the existing charging standards and has high compatibility to facilitate transition and promotion.
1.9.2 Challenges
𖡡 Market promotion
As a new charging standard, it still needs to overcome the challenges of market acceptance and promotion speed.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
It is high-power charging, and the construction cost of charging stations is high, which may affect the speed of initial promotion.
1.9 ChaoJi
Designer
CHAdeMO Association
China Electricity Council (CEC)
Standard
CHAdeMO 3.0
GB/T 20234.3
Charging Type
DC charging
Area of use
China, Japan and other regions.

In 2020, the China Electricity Council (CEC) collaborated with the CHAdeMO Association to launch a high-power fast charging system interface called ChaoJi, also known as CHAdeMO 3.0. The first charging test and demonstration were completed, and the full specifications were officially released in April 2021.
ChaoJi can achieve 500kW high-power charging. The latest version in 2023 is ChaoJi-2/CHAdeMO 3.1, and Ultra-ChaoJi/CHAdeMO 4.0 is also under intensive rapid development.
Source:CHAdeMO Association (visit the website)
1.9.1 Advantages
𖡡 Support ultra-high power charging
The current maximum power can reach 900 kW, which can greatly shorten the charging time and adapt to the charging needs of large-capacity batteries in the future.
𖡡 Unified specifications
Jointly developed by China and Japan, the design is not only compatible with CHAdeMO and GB/T DC but also has a circuit interface design that is compatible with CCS. Therefore, it is regarded as laying the foundation for future global DC charging technology standardization.
𖡡 Compatibility
The design considers the existing charging standards and has high compatibility to facilitate transition and promotion.
1.9.2 Challenges
𖡡 Market promotion
As a new charging standard, it still needs to overcome the challenges of market acceptance and promotion speed.
𖡡 Infrastructure construction costs
It is high-power charging, and the construction cost of charging stations is high, which may affect the speed of initial promotion.
Need more help?
Please submit a business support request and our experts will get in touch with you.
Need more help?
Please submit a business support request and our experts will get in touch with you.




